Spring Special Limited Time 70% Discount Offer - Ends in 0d 00h 00m 00s - Coupon code = getmirror
Pass the CIPS Level 5 Advanced Diploma in Procurement and Supply L5M4 Questions and answers with ExamsMirror
Exam L5M4 Premium Access
View all detail and faqs for the L5M4 exam
662 Students Passed
89% Average Score
95% Same Questions
Organizational strategies can be formed at three different levels within a business. Outline these three levels and explain the benefits of strategy alignment within an organization (25 points)
Options:
See the answer in Explanation below:
Part 1: Outline of the Three Levels of StrategyOrganizational strategies are developed at three distinct levels, each with a specific focus:
Corporate Level Strategy
Step 1: Define the LevelFocuses on the overall direction and scope of the organization (e.g., what businesses to operate in).
Step 2: ExamplesDecisions like diversification, mergers, or market expansion.
Outcome:Sets the long-term vision and portfolio of the business.
Business Level Strategy
Step 1: Define the LevelConcentrates on how to compete in specific markets or industries (e.g., cost leadership, differentiation).
Step 2: ExamplesPricing strategies or product innovation to gain market share.
Outcome:Defines competitive positioning within a business unit.
Functional Level Strategy
Step 1: Define the LevelFocuses on operational execution within departments (e.g., procurement, HR, marketing).
Step 2: ExamplesOptimizing supply chain processes or improving staff training.
Outcome:Supports higher-level goals through tactical actions.
Part 2: Benefits of Strategy Alignment
Step 1: Unified DirectionEnsures all levels work toward common goals, reducing conflicts (e.g., procurement aligns with corporate growth plans).
Step 2: Resource EfficiencyAllocates resources effectively by prioritizing aligned objectives over siloed efforts.
Step 3: Enhanced PerformanceImproves outcomes as coordinated strategies amplify impact (e.g., cost savings at functional level support business competitiveness).
Outcome:Creates a cohesive, high-performing organization.
Exact Extract Explanation:
The CIPS L5M4 Study Guide addresses strategic levels and alignment:
Three Levels:"Corporate strategy defines the organization’s scope, business strategy focuses on competition, and functional strategy supports through operational excellence" (CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 1, Section 1.5).
Alignment Benefits:"Strategy alignment ensures consistency, optimizes resource use, and enhances overall performance" (CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 1, Section 1.6).This is critical for procurement to align with organizational objectives. References: CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 1: Organizational Objectives and Financial Management.
A local council is looking at ways it can fund a large construction project they are planning—the building of a new hospital. Discuss ways in which the council could fund the project, and the advantages and disadvantages of this (25 points)
Options:
See the answer in Explanation below:
A local council, operating in the public sector, has several options to fund a large construction project like a new hospital. Below are three funding methods, with their advantages and disadvantages explained step-by-step:
Government Grants or Funding
Step 1: Identify SourceApply for grants from central government or public health budgets allocated for infrastructure.
Step 2: ProcessSubmit detailed proposals outlining costs, benefits, and public value to secureapproval.
Advantages:
No repayment required, preserving council funds.
Aligns with public sector goals of service delivery.
Disadvantages:
Competitive process with uncertain approval.
Strict conditions may limit flexibility in project execution.
Public-Private Partnership (PPP)
Step 1: Establish PartnershipCollaborate with a private firm to finance and build the hospital, with the council leasing it back over time.
Step 2: ProcessNegotiate terms (e.g., Private Finance Initiative—PFI) where the private partner recovers costs via payments or service contracts.
Advantages:
Reduces upfront council expenditure, spreading costs over years.
Leverages private sector expertise and efficiency.
Disadvantages:
Long-term financial commitments increase future budgets.
Potential loss of control over project specifications.
Borrowing (e.g., Municipal Bonds or Loans)
Step 1: Secure FundsIssue bonds to investors or obtain loans from financial institutions, repayable over decades.
Step 2: ProcessGain approval from government regulators and allocate tax revenues for repayment.
Advantages:
Immediate access to large capital for construction.
Retains council ownership of the hospital.
Disadvantages:
Interest payments increase overall project cost.
Debt burden may strain future budgets.
Exact Extract Explanation:
The CIPS L5M4 Study Guide highlights funding options for public sector projects:
Government Grants:"Grants provide non-repayable funds but often come with stringent compliance requirements" (CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 4, Section 4.4).
PPP:"Public-private partnerships enable infrastructure development without immediate fiscal pressure, though long-term costs can escalate" (CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 4, Section 4.5).
Borrowing:"Borrowing via bonds or loans is common for public bodies, offering flexibility but adding debt obligations" (CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 4, Section 4.2).These align with the public sector’s focus on value for money and service provision. References: CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 4: Sources of Finance.===========
Describe 5 parts of the analysis model, first put forward by Porter, in which an organisation can assess the competitive marketplace (25 marks)
Options:
See the answer in Explanation below:
The analysis model referred to in the question is Porter’s Five Forces, a framework developed by Michael Porter to assess the competitive environment of an industry and understand the forces that influence an organization’s ability to compete effectively. In the context of the CIPS L5M4 Advanced Contract and Financial Management study guide, Porter’s Five Forces is a strategic tool used to analyze the marketplace to inform procurement decisions, supplier selection, and contract strategies, ensuring financial and operational efficiency. Below are the five parts of the model, explained in detail:
Threat of New Entrants:
Description: This force examines how easy or difficult it is for new competitors to enter the market. Barriers to entry (e.g., high capital requirements, brand loyalty, regulatory restrictions) determine the threat level.
Impact: High barriers protect existing players, while low barriers increase competition, potentially driving down prices and margins.
Example: In the pharmaceutical industry, high R&D costs and strict regulations deter new entrants, reducing the threat.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers:
Description: This force assesses the influence suppliers have over the industry, based on their number, uniqueness of offerings, and switching costs for buyers.
Impact: Powerful suppliers can increase prices or reduce quality, squeezing buyer profitability.
Example: In the automotive industry, a limited number of specialized steel suppliers may have high bargaining power, impacting car manufacturers’ costs.
Bargaining Power of Buyers:
Description: This force evaluates the influence buyers (customers) have on the industry, determined by their number, purchase volume, and ability to switch to alternatives.
Impact: Strong buyer power can force price reductions or demand higher quality, reducing profitability.
Example: In retail, large buyers like supermarkets can negotiate lower prices from suppliers due to their high purchase volumes.
Threat of Substitute Products or Services:
Description: This force analyzes the likelihood of customers switching to alternative products or services that meet the same need, based on price, performance, or availability.
Impact: A high threat of substitutes limits pricing power and profitability.
Example: In the beverage industry, the rise of plant-based milk (e.g., almond milk) poses a substitute threat to traditional dairy milk.
Competitive Rivalry within the Industry:
Description: This force examines the intensity of competition among existing firms, influenced by the number of competitors, market growth, and product differentiation.
Impact: High rivalry leads to price wars, increased marketing costs, or innovation pressures, reducing profitability.
Example: In the smartphone industry, intense rivalry between Apple and Samsung drives innovation but also squeezes margins through competitive pricing.
Exact Extract Explanation:
The CIPS L5M4 Advanced Contract and Financial Management study guide explicitly references Porter’s Five Forces as a tool for "analyzing the competitive environment" to inform procurement and contract strategies. It is presented in the context of market analysis, helping organizations understand external pressures that impact supplier relationships, pricing, and financial outcomes. The guide emphasizes its relevance in strategic sourcing (as in Question 11) and risk management, ensuring buyers can negotiate better contracts and achieve value for money.
Detailed Explanation of Each Force:
Threat of New Entrants:
The guide notes that "barriers to entry influence market dynamics." For procurement, a low threat (e.g., due to high entry costs) means fewer suppliers, potentially increasing supplier power and costs. A buyer might use this insight to secure long-term contracts with existing suppliers to lock in favorable terms.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers:
Chapter 2 highlights that "supplier power affects cost structures." In L5M4, this is critical for financial management—high supplier power (e.g., few suppliers of a rare material) can inflate costs, requiring buyers to diversify their supply base or negotiate harder.
Bargaining Power of Buyers:
The guide explains that "buyer power impacts pricing and margins." For a manufacturer like XYZ Ltd (Question 7), strong buyer power from large clients might force them to source cheaper raw materials, affecting supplier selection.
Threat of Substitute Products or Services:
L5M4’s risk management section notes that "substitutes can disrupt supply chains." A high threat (e.g., synthetic alternatives to natural materials) might push a buyer to collaborate with suppliers on innovation to stay competitive.
Competitive Rivalry within the Industry:
The guide states that "rivalry drives market behavior." High competition might lead to price wars, prompting buyers to seek cost efficiencies through strategic sourcing or supplier development (Questions 3 and 11).
Application in Contract Management:
Porter’s Five Forces helps buyers assess the marketplace before entering contracts. For example, if supplier power is high (few suppliers), a buyer might negotiate longer-term contracts to secure supply. If rivalry is intense, they might prioritize suppliers offering innovation to differentiate their products.
Financially, understanding these forces ensures cost control—e.g., mitigatingsupplier power reduces cost inflation, aligning with L5M4’s focus on value for money.
Practical Example for XYZ Ltd (Question 7):
Threat of New Entrants: Low, due to high setup costs for raw material production, giving XYZ Ltd fewer supplier options.
Supplier Power: High, if raw materials are scarce, requiring XYZ Ltd to build strong supplier relationships.
Buyer Power: Moderate, as XYZ Ltd’s clients may have alternatives, pushing for competitive pricing.
Substitutes: Low, if raw materials are specialized, but XYZ Ltd should monitor emerging alternatives.
Rivalry: High, in manufacturing, so XYZ Ltd must source efficiently to maintain margins.
This analysis informs XYZ Ltd’s supplier selection and contract terms, ensuring financial and operational resilience.
Broader Implications:
The guide advises using Porter’s Five Forces alongside other tools (e.g., SWOT analysis) for a comprehensive market view. It also stresses that these forces are dynamic—e.g., new regulations might lower entry barriers, increasing competition over time.
In financial management, the model helps buyers anticipate cost pressures (e.g., from supplier power) and negotiate contracts that mitigate risks, ensuring long-term profitability.
Explain three different types of financial data you could collect on a supplier and what this data would tell you (25 marks)
Options:
See the answer in Explanation below:
Collecting financial data on a supplier is a critical step in supplier evaluation, ensuring they are financially stable and capable of fulfilling contractual obligations. In the context of the CIPS L5M4 Advanced Contract and Financial Management study guide, analyzing financial data helps mitigate risks, supports strategic sourcing decisions, and ensures value for money in contracts. Below are three types of financial data, their purpose, and what they reveal about a supplier, explained in detail:
Profitability Ratios (e.g., Net Profit Margin):
Description: Profitability ratios measure a supplier’s ability to generate profit from its operations. Net Profit Margin, for example, is calculated as:
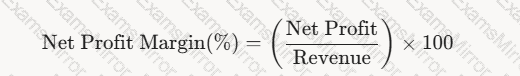 A math equation with numbers and symbols
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A math equation with numbers and symbols
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
This data is typically found in the supplier’s income statement.
What It Tells You:
Indicates the supplier’s financial health and efficiency in managing costs. A high margin (e.g., 15%) suggests strong profitability and resilience, while a low or negative margin (e.g., 2% or -5%) signals potential financial distress.
Helps assess if the supplier can sustain operations without passing excessive costs to the buyer.
Example: A supplier with a 10% net profit margin is likely stable, but a declining margin over years might indicate rising costs or inefficiencies, posing a risk to contract delivery.
Liquidity Ratios (e.g., Current Ratio):
Description: Liquidity ratios assess a supplier’s ability to meet short-term obligations. The Current Ratio is calculated as:
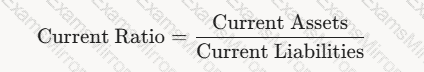 A black text on a white background
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A black text on a white background
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
This data is sourced from the supplier’s balance sheet.
What It Tells You:
Shows whether the supplier can pay its debts as they come due. A ratio above 1 (e.g., 1.5) indicates good liquidity, while a ratio below 1 (e.g., 0.8) suggests potential cash flow issues.
A low ratio may signal risk of delays or failure to deliver due to financial constraints.
Example: A supplier with a Current Ratio of 2.0 can comfortably cover short-term liabilities, reducing the risk of supply disruptions for the buyer.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio:
Description: This ratio measures a supplier’s financial leverage by comparing its total debt to shareholders’ equity:
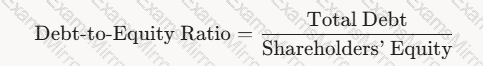 A math equation with black text
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A math equation with black text
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
This data is also found in the balance sheet.
What It Tells You:
Indicates the supplier’s reliance on debt financing. A high ratio (e.g., 2.0) suggests heavy borrowing, increasing financial risk, while a low ratio (e.g., 0.5) indicates stability.
A high ratio may mean the supplier is vulnerable to interest rate hikes or economic downturns, risking insolvency.
Example: A supplier with a Debt-to-Equity Ratio of 0.3 is financially stable, while one with a ratio of 3.0 might struggle to meet obligations if market conditions worsen.
Exact Extract Explanation:
The CIPS L5M4 Advanced Contract and Financial Management study guide emphasizes the importance of financial due diligence in supplier selection and risk management, directly addressing the need to collect and analyze financial data. It highlights that "assessing a supplier’s financial stability is critical to ensuring contract performance and mitigating risks," particularly in strategic or long-term contracts. The guide specifically references financial ratios as tools to evaluate supplier health, aligning with the types of data above.
Detailed Explanation of Each Type of Data:
Profitability Ratios (e.g., Net Profit Margin):
The guide notes that profitability metrics like Net Profit Margin "provide insight into a supplier’s operational efficiency and financial sustainability." A supplier with consistent or growing margins is likely to maintain quality and delivery standards, supporting contract reliability.
Application: For XYZ Ltd (Question 7), a raw material supplier with a declining margin might cut corners on quality to save costs, risking production issues. L5M4 stresses that profitability data helps buyers predict long-term supplier viability, ensuring financial value.
Liquidity Ratios (e.g., Current Ratio):
Chapter 4 of the study guide highlights liquidity as a "key indicator of short-term financial health." A supplier with poor liquidity might delay deliveries or fail to fulfill orders, directly impacting the buyer’s operations and costs.
Practical Use: A Current Ratio below 1 might prompt XYZ Ltd to negotiate stricter payment terms or seek alternative suppliers, aligning with L5M4’s focus on risk mitigation. The guide advises using liquidity data to avoid over-reliance on financially weak suppliers.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio:
The guide identifies leverage ratios like Debt-to-Equity as measures of "financial risk exposure." A high ratio indicates potential instability, which could lead to supply chain disruptions if the supplier faces financial distress.
Relevance: For a manufacturer like XYZ Ltd, a supplier with a high Debt-to-Equity Ratio might be a risk during economic downturns, as they may struggle to access credit for production. The guide recommends using this data to assess long-term partnership potential, a key financial management principle.
Broader Implications:
The guide advises combining these financial metrics for a comprehensive view. For example, a supplier with high profitability but poor liquidity might be profitable but unable to meet short-term obligations, posing a contract risk.
Financial data should be tracked over time (e.g., 3-5 years) to identify trends—e.g., a rising Debt-to-Equity Ratio might signal increasing risk, even if current figures seem acceptable.
In L5M4’s financial management context, this data ensures cost control by avoiding suppliers likely to fail, which could lead to costly delays or the need to source alternatives at higher prices.
Practical Application for XYZ Ltd:
Profitability: A supplier with a 12% Net Profit Margin indicates stability, but XYZ Ltd should monitor for declines.
Liquidity: A Current Ratio of 1.8 suggests the supplier can meet obligations, reducing delivery risks.
Debt-to-Equity: A ratio of 0.4 shows low leverage, making the supplier a safer long-term partner.
Together, these metrics help XYZ Ltd select a financially sound supplier, ensuring contract performance and financial efficiency.
Describe 5 ways in which you could track the performance of a services contract such as the provision of IT services to an office. (25 marks)
Options:
See the answer in Explanation below:
Tracking the performance of a services contract, such as the provision of IT services to an office, requires robust methods to ensure the supplier meets operational, financial, and contractual expectations. The CIPS L5M4 Advanced Contract and Financial Management study guide underscores the importance of systematic monitoring to achieve value for money and maintain service quality. Below are five comprehensive ways to track performance, detailed step-by-step:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
Description: Establish specific, measurable metrics tied to contract objectives to evaluate service delivery consistently.
Application: For IT services, KPIs could include system uptime (e.g., 99.9% availability), average resolution time for incidents (e.g., under 2 hours), or first-call resolution rate (e.g., 90% of issues resolved on initial contact).
Process: Use automated tools like IT service management (ITSM) software (e.g., ServiceNow) to collect data, generating regular reports for review.
Outcome: Provides quantifiable evidence of performance, enabling proactive management of service levels and cost efficiency.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) Monitoring:
Description: Track adherence to predefined service standards outlined in SLAs within the contract.
Application: An SLA might require critical IT issues to be addressed within 30 minutes or ensure no more than 1 hour of unplanned downtime per month.
Process: Monitor compliance using ticketing systems or logs, comparing actual performance against SLA targets, with escalation procedures for breaches.
Outcome: Ensures contractual commitments are met, with mechanisms like penalties or credits to enforce accountability.
Regular Performance Reviews and Audits:
Description: Conduct scheduled evaluations and audits to assess both qualitative and quantitative aspects of service delivery.
Application: Monthly reviews might analyze incident trends or user complaints, while an annual audit could verify cybersecurity compliance (e.g., ISO 27001 standards).
Process: Hold meetings with the supplier, review performance data, and audit processes or systems using checklists or third-party assessors.
Outcome: Offers a holistic view of performance, fostering collaboration and identifying improvement opportunities.
User Feedback and Satisfaction Surveys:
Description: Collect feedback from office staff (end-users) to gauge the perceived quality and effectiveness of IT services.
Application: Surveys might ask users to rate helpdesk responsiveness (e.g., 4.5/5) or system reliability, with qualitative comments on pain points.
Process: Distribute surveys quarterly via email or an internal portal, analyze results, and discuss findings with the supplier.
Outcome: Captures user experience, providing insights that quantitative metrics might miss, such as staff morale impacts.
Financial Performance Tracking:
Description: Monitor costs and financial outcomes to ensure the contract remains within budget and delivers economic value.
Application: Track metrics like cost per service ticket (e.g., $40 per incident), total expenditure vs. budget (e.g., within 2% variance), or savings from preventive maintenance (e.g., 10% reduction in repair costs).
Process: Review invoices, cost reports, and benchmark against industry standards or previous contracts.
Outcome: Aligns service performance with financial goals, ensuring cost-effectiveness over the contract lifecycle.
Exact Extract Explanation:
The CIPS L5M4 Advanced Contract and Financial Management study guide positions performance tracking as a critical activity to "ensure supplier accountability and value delivery" in services contracts. Unlike goods-based contracts, services like IT provision require ongoing monitoring due to their intangible nature and reliance on consistent delivery. The guide provides frameworks for measuring performance, which these five methods reflect.
Way 1: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
The guide describes KPIs as "essential tools for monitoring contract performance" (Chapter 2). For IT services, it suggests metrics like "service availability" (e.g., uptime) and "response times" to assess operational success.
Detailed Use: A KPI of 99.9% uptime ensures minimal disruption to office productivity, while a 90% first-call resolution rate reduces downtime costs. The guide stresses that KPIs must be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) and agreed upon during contract negotiation.
Financial Tie-In: Efficient KPIs lower operational costs (e.g., fewer escalations), aligning with L5M4’s focus on financial management.
Way 2: Service Level Agreements (SLAs) Monitoring:
SLAs are highlighted as "contractual benchmarks" that define acceptable service levels (Chapter 2). For IT contracts, the guide recommends SLAs like "maximumdowntime" or "incident response time" to enforce standards.
Implementation: Monitoring via ITSM tools tracks SLA breaches (e.g., a 30-minute response target missed), triggering penalties or corrective actions. The guide notes SLAs "provide clarity and enforceability," critical for service reliability.
Outcome: Ensures financial penalties deter poor performance, protecting the buyer’s investment.
Way 3: Regular Performance Reviews and Audits:
The guide advocates "structured reviews" to evaluate supplier performance beyond metrics (Chapter 2). For IT services, reviews might assess trends (e.g., recurring outages), while audits verify compliance with security or data protection standards.
Practical Approach: Monthly meetings with the supplier review KPI/SLA data, while an audit might check server logs for uptime claims. The guide emphasizes audits for "high-risk contracts" like IT, where breaches could be costly.
Benefit: Balances operational oversight with financial risk management, a core L5M4 principle.
Way 4: User Feedback and Satisfaction Surveys:
Chapter 2 notes that "end-user satisfaction" is vital for services contracts, as it reflects real-world impact. The guide suggests surveys to capture qualitative data, complementing KPIs/SLAs.
Execution: A survey rating helpdesk support at 4/5 might reveal delays not evident in response time metrics. The guide advises using feedback to "refine service delivery," ensuring user needs are met.
Value: Links service quality to staff productivity, indirectly affecting financial outcomes (e.g., reduced downtime).
Way 5: Financial Performance Tracking:
The guide’s financial management section (Chapter 4) stresses tracking costs to ensure "value for money." For IT services, this includes monitoring direct costs (e.g., support fees) and indirect benefits (e.g., savings from fewer incidents).
Application: Benchmarking cost per ticket against industry norms (e.g., $40 vs. $50 average) ensures competitiveness. The guide advises analyzing "total cost of ownership" to capture long-term value.
Alignment: Ensures the contract remains financially viable, a key L5M4 objective.
Broader Implications:
These methods should be integrated into a performance management framework, with clear roles (e.g., contract manager overseeing reviews) and tools (e.g., software for KPI tracking).
The guide warns against over-reliance on one method—combining KPIs, SLAs, reviews, feedback, and financial data provides a balanced view.
For IT services, performance tracking must adapt to evolving needs (e.g., new software rollouts), reflecting L5M4’s emphasis on flexibility in contract management.
XYZ Ltd is a retail organization that is conducting a competitive benchmarking project. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this? (25 points)
Options:
See the answer in Explanation below:
Competitive benchmarking involves XYZ Ltd comparing its performance with a rival retailer. Below are the advantages and disadvantages, explained step-by-step:
Advantages
Identifies Competitive Gaps
Step 1: ComparisonXYZ assesses metrics like pricing, delivery speed, or customer service against a competitor.
Step 2: OutcomeHighlights areas where XYZ lags (e.g., slower delivery), driving targeted improvements.
Benefit:Enhances market positioning.
Drives Performance Improvement
Step 1: LearningAdopting best practices from competitors (e.g., efficient inventory management).
Step 2: OutcomeBoosts operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Benefit:Strengthens competitiveness in retail.
Market Insight
Step 1: AnalysisProvides data on industry standards and trends.
Step 2: OutcomeInforms strategic decisions (e.g., pricing adjustments).
Benefit:Keeps XYZ aligned with market expectations.
Disadvantages
Data Access Challenges
Step 1: LimitationCompetitors may not share detailed performance data.
Step 2: OutcomeRelies on estimates or public info, reducing accuracy.
Drawback:Limits depth of comparison.
Risk of Imitation Over Innovation
Step 1: FocusCopying rivals may overshadow unique strategies.
Step 2: OutcomeXYZ might lose differentiation (e.g., unique branding).
Drawback:Stifles originality.
Resource Intensive
Step 1: EffortRequires time, staff, and costs to gather and analyze data.
Step 2: OutcomeDiverts resources from other priorities.
Drawback:May strain operational capacity.
Exact Extract Explanation:
The CIPS L5M4 Study Guide discusses competitive benchmarking:
Advantages:"It identifies gaps, improves performance, and provides market insights" (CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 2, Section 2.6).
Disadvantages:"Challenges include limited data access, potential over-reliance on imitation, and high resource demands" (CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 2, Section 2.6).This is key for retail procurement and financial strategy. References: CIPS L5M4 StudyGuide, Chapter 2: Supply Chain Performance Management.===========
Discuss four factors which may influence supply and demand in foreign exchange (25 points)
Options:
See the answer in Explanation below:
The supply and demand for foreign exchange (FX) determine currency exchange rates, influenced by various economic and external factors. Below are four key factors, explained step-by-step:
Interest Rates
Step 1: Understand the MechanismHigher interest rates in a country attract foreign investors seeking better returns, increasing demand for that currency.
Step 2: ImpactFor example, if the UK raises rates, demand for GBP rises as investors buy GBP to invest in UK assets, while supply of other currencies increases.
Step 3: OutcomeStrengthens the currency with higher rates, shifting FX equilibrium.
Inflation Rates
Step 1: Understand the MechanismLower inflation preserves a currency’s purchasing power, boosting demand, while high inflation increases supply as holders sell off.
Step 2: ImpactA country with low inflation (e.g., Japan) sees higher demand for its yen compared to a high-inflation country.
Step 3: OutcomeLow inflation strengthens a currency; high inflation weakens it.
Trade Balance
Step 1: Understand the MechanismA trade surplus (exports > imports) increases demand for a country’s currency as foreign buyers convert their money to pay exporters.
Step 2: ImpactA US trade surplus increases USD demand; a deficit increases USD supply as imports require foreign currency.
Step 3: OutcomeSurplus strengthens, deficit weakens the currency.
Political Stability
Step 1: Understand the MechanismStable governments attract foreign investment, increasing currency demand; instability prompts capital flight, raising supply.
Step 2: ImpactPolitical unrest in a country (e.g., election uncertainty) may lead to selling its currency, reducing demand.
Step 3: OutcomeStability bolsters, instability depresses currency value.
Exact Extract Explanation:
The CIPS L5M4 Study Guide outlines these factors as critical to FX markets:
Interest Rates:"Higher rates increase demand for a currency by attracting capital inflows" (CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 5, Section 5.5).
Inflation Rates:"Relative inflation impacts currency value, with lower rates enhancing demand" (CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 5, Section 5.5).
Trade Balance:"A positive trade balance boosts currency demand; deficits increase supply" (CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 5, Section 5.5).
Political Stability:"Stability encourages investment, while uncertainty drives currency sell-offs" (CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 5, Section 5.5).These factors are essential for procurement professionals managing international contracts. References: CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 5: Managing Foreign Exchange Risks.===========
Explain what is meant by ‘supplier selection’ (25 marks)
Options:
See the answer in Explanation below:
Supplier selection is a critical process in procurement and contract management, involving the evaluation and choice of suppliers to meet an organization’s needs for goods, services, or materials. In the context of the CIPS L5M4 Advanced Contract and Financial Management study guide, supplier selection is a strategic activity that ensures suppliers align with financial, operational, and strategic objectives, delivering value for money and minimizing risks. Below is a detailed explanation, broken down step-by-step:
Definition:
Supplier selection is the process of identifying, evaluating, and choosing suppliers based on predefined criteria to fulfill an organization’s procurement requirements.
It involves assessing potential suppliers’ capabilities, performance, and alignment with the buyer’s goals.
Purpose:
Ensures the selected supplier can deliver the right quality, quantity, and timing of goods or services while meeting financial and contractual expectations.
Aims to minimize risks (e.g., supply disruptions) and maximize value (e.g., cost efficiency, innovation).
Example: XYZ Ltd (Question 7) selects a raw material supplier based on cost, quality, and reliability.
Key Steps in Supplier Selection:
Identify Needs: Define the organization’s requirements (e.g., specific raw materials, delivery schedules).
Develop Criteria: Establish evaluation criteria (e.g., cost, quality, financial stability—see Questions 7 and 13).
Source Potential Suppliers: Use competitive (Question 16) or non-competitive sourcing to create a shortlist.
Evaluate Suppliers: Assess candidates against criteria using tools like scorecards or financial analysis.
Negotiate and Select: Choose the best supplier and negotiate contract terms.
Example: Rachel (Question 17) might shortlist suppliers for raw materials, evaluate them on price and delivery, and select the one offering the best overall value.
Importance in Contract Management:
Supplier selection directly impacts contract performance—choosing the wrong supplier can lead to delays, quality issues, or cost overruns.
It aligns with financial management by ensuring cost efficiency and risk mitigation, key L5M4 principles.
Example: Selecting a financially stable supplier (Question 13) reduces the risk of mid-contract failure.
Strategic Considerations:
Involves balancing short-term needs (e.g., immediate cost savings) with long-term goals (e.g., supplier innovation—Question 2).
May incorporate strategic sourcing principles (Question 11) to align with organizational objectives like sustainability or innovation.
Example: A company might select a supplier with strong innovation capacity to support future product development.
Exact Extract Explanation:
The CIPS L5M4 Advanced Contract and Financial Management study guide defines supplier selection as "the process of evaluating and choosing suppliers to meet organizational needs while ensuring value for money and minimizing risks." It is a foundational element of procurement, discussed extensively in the context of performance management, risk mitigation, and financial efficiency. The guide emphasizes that supplier selection is not just about cost but involves a "structured evaluation" to ensure suppliers deliver on quality, reliability, and strategic objectives.
Detailed Explanation:
The guide outlines supplier selection as a multi-step process, starting with "defining requirements" and ending with "contract award." This structured approach ensures fairness and alignment with organizational goals.
Chapter 2 stresses that supplier selection should use "robust criteria" (e.g., cost, quality, financial stability—Question 7) to evaluate candidates, often through tools like weighted scorecards or financial analysis (Question 13).
The guide links supplier selection to financial management by noting its role in "cost control" and "risk reduction." For instance, selecting a supplier with a strong Current Ratio (Question 13) ensures they can meet short-term obligations, avoiding supply disruptions that could inflate costs.
It also highlights the strategic aspect, integrating concepts like innovation capacity (Question 2) and industry analysis (Question 14) to select suppliers who support long-term goals, such as sustainability or technological advancement.
Practical Application:
For Rachel (Question 17), supplier selection for raw materials involves defining needs (e.g., consistent steel supply), setting criteria (e.g., price, quality, delivery), shortlisting suppliers, evaluating them (e.g., via financial data), and choosing the best fit. This ensures her manufacturing operations run smoothly and cost-effectively.
The guide advises involving cross-functional teams (e.g., procurement, production, finance) to ensure criteria reflect organizational priorities, enhancing the selection process’s effectiveness.
Broader Implications:
Supplier selection impacts the entire contract lifecycle—poor selection can lead to performance issues, requiring corrective actions like supplier development (Question 3).
Financially, it ensures value for money by selecting suppliers who offer the best balance of cost, quality, and reliability, aligning with L5M4’s core focus.
The guide also notes that selection should be revisited periodically, as market conditions (Question 14) or supplier performance may change, requiring adjustments to maintain contract success.
What are three financial risks in exchange rate changes and how might an organization overcome these? (25 points)
Options:
See the answer in Explanation below:
Exchange rate changes pose financial risks to organizations engaged in international trade. Below are three risks and mitigation strategies, explained step-by-step:
Transaction Risk
Step 1: Define the RiskLoss from exchange rate fluctuations between invoicing and payment (e.g., a stronger supplier currency increases costs).
Step 2: MitigationUse forward contracts to lock in rates at the time of contract agreement.
Step 3: OutcomeEnsures predictable costs, avoiding cash flow disruptions.
Translation Risk
Step 1: Define the RiskImpact on financial statements when converting foreign subsidiary earnings to the home currency (e.g., weaker foreign currency reduces reported profits).
Step 2: MitigationHedge via currency swaps or maintain natural hedges (e.g., matching foreign assets and liabilities).
Step 3: OutcomeStabilizes reported earnings, aiding financial planning.
Economic Risk
Step 1: Define the RiskLong-term currency shifts affecting competitiveness (e.g., a stronger home currency makes exports pricier).
Step 2: MitigationDiversify operations or sourcing across countries to spread exposure.
Step 3: OutcomeReduces reliance on any single currency’s performance.
Exact Extract Explanation:
The CIPS L5M4 Study Guide identifies these risks and solutions:
Transaction Risk:"Arises from timing differences in international payments, mitigated by forwards" (CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 5, Section 5.1).
Translation Risk:"Affects consolidated accounts and can be managed through hedging or balance sheet strategies" (CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 5, Section 5.1).
Economic Risk:"Long-term exposure requires strategic diversification" (CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 5, Section 5.1).These align with managing FX volatility in procurement. References: CIPS L5M4 Study Guide, Chapter 5: Managing Foreign Exchange Risks.===========
Describe what is meant by ‘Supply Chain Integration’ (8 marks). How would a buyer go about implementing this approach and what benefits could be gained from it? (17 marks).
Options:
See the answer in Explanation below:
Part 1: Describe what is meant by ‘Supply Chain Integration’ (8 marks)
Supply Chain Integration (SCI) refers to the seamless coordination and alignment of processes, information, and resources across all parties in a supply chain—suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and buyers—to achieve a unified, efficient system. In the context of the CIPS L5M4 Advanced Contract and Financial Management study guide, SCI emphasizes collaboration to optimize performance and deliver value. Below is a step-by-step explanation:
Definition:
SCI involves linking supply chain partners to work as a cohesive unit, sharing goals, data, and strategies.
It spans upstream (suppliers) and downstream (customers) activities.
Purpose:
Aims to eliminate silos, reduce inefficiencies, and enhance responsiveness to market demands.
Example: A buyer and supplier share real-time inventory data to prevent stockouts.
Part 2: How would a buyer go about implementing this approach and what benefits could be gained from it? (17 marks)
Implementation Steps:
Establish Collaborative Relationships:
Build trust and partnerships with suppliers through regular communication and joint planning.
Example: Set up quarterly strategy meetings with key suppliers.
Implement Information Sharing Systems:
Use technology (e.g., ERP systems, cloud platforms) to share real-time data on demand, inventory, and forecasts.
Example: Integrate a supplier’s system with the buyer’s to track orders live.
Align Objectives and KPIs:
Agree on shared goals and performance metrics (e.g., delivery speed, cost reduction) to ensure mutual accountability.
Example: Both parties target a 95% on-time delivery rate.
Streamline Processes:
Redesign workflows (e.g., joint procurement or production planning) to eliminate redundancies.
Example: Co-develop a just-in-time delivery schedule.
Benefits:
Improved Efficiency:
Streamlined operations reduce waste and lead times.
Example: Cutting order processing time from 5 days to 2 days.
Cost Savings:
Better coordination lowers inventory holding costs and optimizes resource use.
Example: Reducing excess stock by 20% through shared forecasting.
Enhanced Responsiveness:
Real-time data enables quick adaptation to demand changes.
Example: Adjusting supply within 24 hours of a sales spike.
Stronger Relationships:
Collaboration fosters trust and long-term supplier commitment.
Example: A supplier prioritizes the buyer during shortages.
Exact Extract Explanation:
Part 1: What is Supply Chain Integration?
The CIPS L5M4 Advanced Contract and Financial Management study guide does not dedicate a specific section to SCI but embeds it within discussions on supplier relationships and performance optimization. It describes SCI as "the alignment of supply chain activities to achieve a seamless flow of goods, services, and information." The guide positions it as a strategic approach to enhance contract outcomes by breaking down barriers between supply chain partners, aligning with its focus on value delivery and financial efficiency.
Detailed Explanation:
SCI integrates processes like procurement, production, and logistics across organizations. The guide notes that "effective supply chains require coordination beyond contractual obligations," emphasizing shared goals over transactional interactions.
For example, a manufacturer (buyer) integrating with a raw material supplier ensures materials arrive just as production ramps up, avoiding delays or overstocking. This reflects L5M4’s emphasis on operational and financial synergy.
Part 2: Implementation and Benefits
The study guide highlights SCI as a means to "maximize efficiency and value," linking it to contract management and financial performance. It provides implicit guidance on implementation and benefits through its focus on collaboration and performance metrics.
Implementation Steps:
Establish Collaborative Relationships:
Chapter 2 stresses "partnership approaches" to improve supplier performance. This starts with trust-building activities like joint workshops, aligning with SCI’s collaborative ethos.
Implement Information Sharing Systems:
The guide advocates "technology-enabled transparency" (e.g., shared IT platforms) to enhance visibility, a cornerstone of SCI. This reduces guesswork and aligns supply with demand.
Align Objectives and KPIs:
L5M4 emphasizes "mutually agreed performance measures" (e.g., KPIs like delivery accuracy). SCI requires this alignment to ensure all parties work toward common outcomes.
Streamline Processes:
The guide suggests "process optimization" through collaboration, such assynchronized planning, to eliminate inefficiencies—a practical step in SCI.
Benefits:
Improved Efficiency:
The guide links integrated processes to "reduced cycle times," a direct outcome of SCI. For instance, shared data cuts delays, aligning with operational goals.
Cost Savings:
Chapter 4 highlights "minimizing waste" as a financial management priority. SCI reduces excess inventory and transport costs, delivering tangible savings.
Enhanced Responsiveness:
The guide notes that "agile supply chains adapt to market shifts," a benefit of SCI’s real-time coordination. This supports competitiveness, a strategic L5M4 focus.
Stronger Relationships:
Collaboration "builds resilience and trust," per the guide. SCI fosters partnerships, ensuring suppliers prioritize the buyer’s needs, enhancing contract stability.
Practical Application:
For XYZ Ltd (from Question 7), SCI might involve integrating a raw material supplier into their production planning. Implementation includes an ERP link for inventory data, aligned KPIs (e.g., 98% delivery reliability), and joint scheduling. Benefits could include a 15% cost reduction, 3-day faster lead times, and a supplier committed to priority service during peak demand.
The guide advises balancing integration costs (e.g., IT investment) with long-term gains, a key financial consideration in L5M4.
Modal title
TOP CODES
Top selling exam codes in the certification world, popular, in demand and updated to help you pass on the first try.
