Spring Special Limited Time 70% Discount Offer - Ends in 0d 00h 00m 00s - Coupon code = getmirror
Pass the Databricks ML Data Scientist Databricks-Machine-Learning-Associate Questions and answers with ExamsMirror
Exam Databricks-Machine-Learning-Associate Premium Access
View all detail and faqs for the Databricks-Machine-Learning-Associate exam
750 Students Passed
89% Average Score
92% Same Questions
The implementation of linear regression in Spark ML first attempts to solve the linear regression problem using matrix decomposition, but this method does not scale well to large datasets with a large number of variables.
Which of the following approaches does Spark ML use to distribute the training of a linear regression model for large data?
A data scientist has written a data cleaning notebook that utilizes the pandas library, but their colleague has suggested that they refactor their notebook to scale with big data.
Which of the following approaches can the data scientist take to spend the least amount of time refactoring their notebook to scale with big data?
A machine learning engineering team has a Job with three successive tasks. Each task runs a single notebook. The team has been alerted that the Job has failed in its latest run.
Which of the following approaches can the team use to identify which task is the cause of the failure?
A data scientist is wanting to explore the Spark DataFrame spark_df. The data scientist wants visual histograms displaying the distribution of numeric features to be included in the exploration.
Which of the following lines of code can the data scientist run to accomplish the task?
A data scientist wants to parallelize the training of trees in a gradient boosted tree to speed up the training process. A colleague suggests that parallelizing a boosted tree algorithm can be difficult.
Which of the following describes why?
A data scientist wants to use Spark ML to impute missing values in their PySpark DataFrame features_df. They want to replace missing values in all numeric columns in features_df with each respective numeric column’s median value.
They have developed the following code block to accomplish this task:
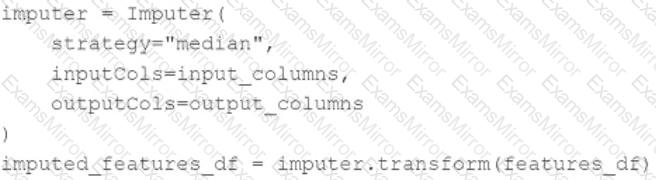
The code block is not accomplishing the task.
Which reasons describes why the code block is not accomplishing the imputation task?
What is the name of the method that transforms categorical features into a series of binary indicator feature variables?
A machine learning engineer is converting a decision tree from sklearn to Spark ML. They notice that they are receiving different results despite all of their data and manually specified hyperparameter values being identical.
Which of the following describes a reason that the single-node sklearn decision tree and the Spark ML decision tree can differ?
Which of the following approaches can be used to view the notebook that was run to create an MLflow run?
The implementation of linear regression in Spark ML first attempts to solve the linear regression problem using matrix decomposition, but this method does not scale well to large datasets with a large number of variables.
Which of the following approaches does Spark ML use to distribute the training of a linear regression model for large data?
TOP CODES
Top selling exam codes in the certification world, popular, in demand and updated to help you pass on the first try.
